Selected Publications
Citations have links, but send an email request if you would like a pdf.Complete list of publications.
 |
Baldassano, JF, MacLeod, KM (2024) Electrophysiological Correlates of divergent projections in the Avian Superior Olivary nucleus. J. Neurophysiology 132(5): 1412-1425. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00099.2024 |
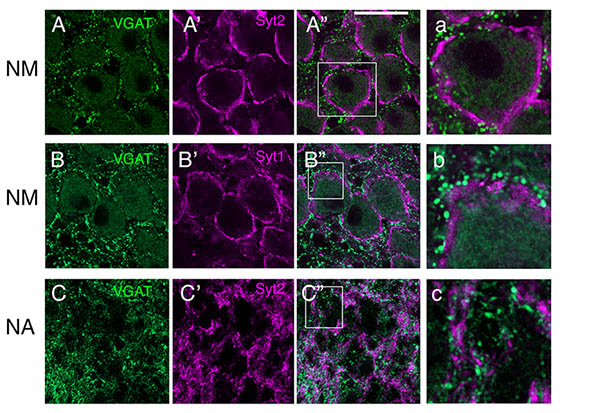 |
MacLeod, K.M., Pandya, S. (2022) Expression and Neurotransmitter Association of the Synaptic Calcium Sensor Synaptotagmin in the Avian Auditory Brain Stem. JARO 23(6): 701-720. doi: 10.1007/s10162-022-00863-1 |
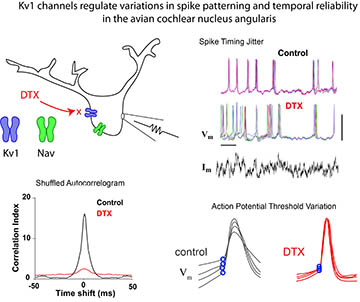 |
Baldassano JF, MacLeod KM. (2022) Kv1 channels regulate variations in spike patterning and temporal reliability in the avian cochlear nucleus angularis. J Neurophysiol. 2022 Jan 1;127(1):116-129. doi: 10.1152/jn.00460.2021 |
 |
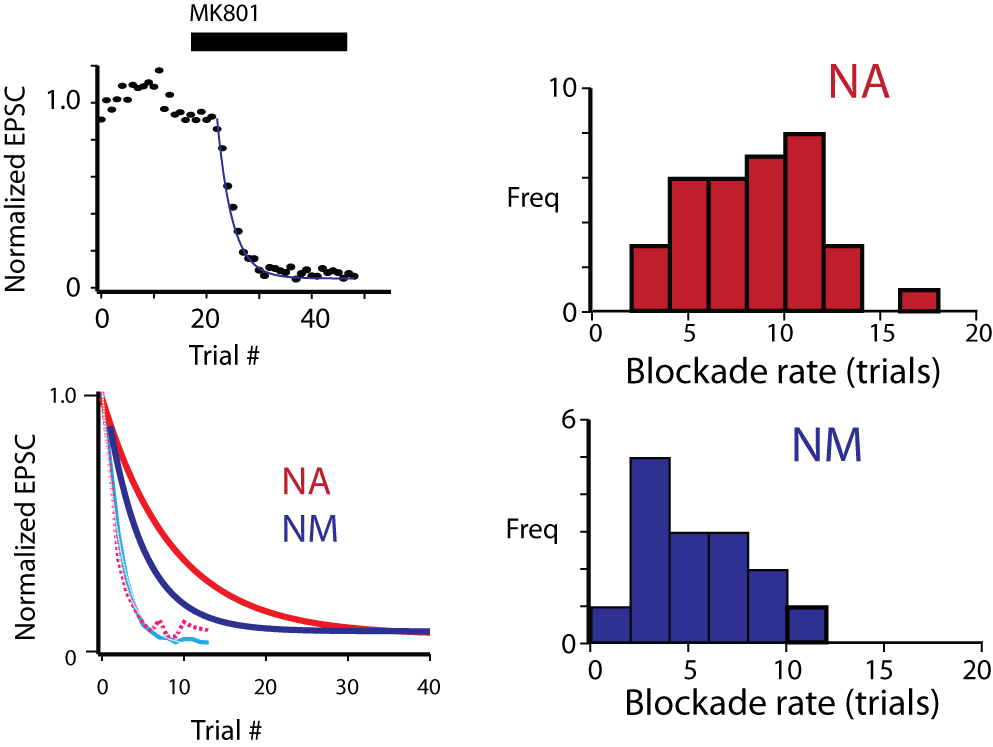
Lubejko, S.T. §, Fontaine, B., Soueidan, S.E., MacLeod, K.M. (2019) Spike threshold adaptation diversifies neuronal operating mode in the auditory brainstem. J. Neurophysiology 122(6): 2576-2590.doi: 10.1152/jn.00234.2019 link |
 |
Ahn. J and K.M. MacLeod. (2016) Target-specific regulation of presynaptic release properties at auditory nerve terminals in the cochlear nucleus J. Neurophysiology 115(3): 1679-90. doi: 10.1152/jn.00752.2015 link |
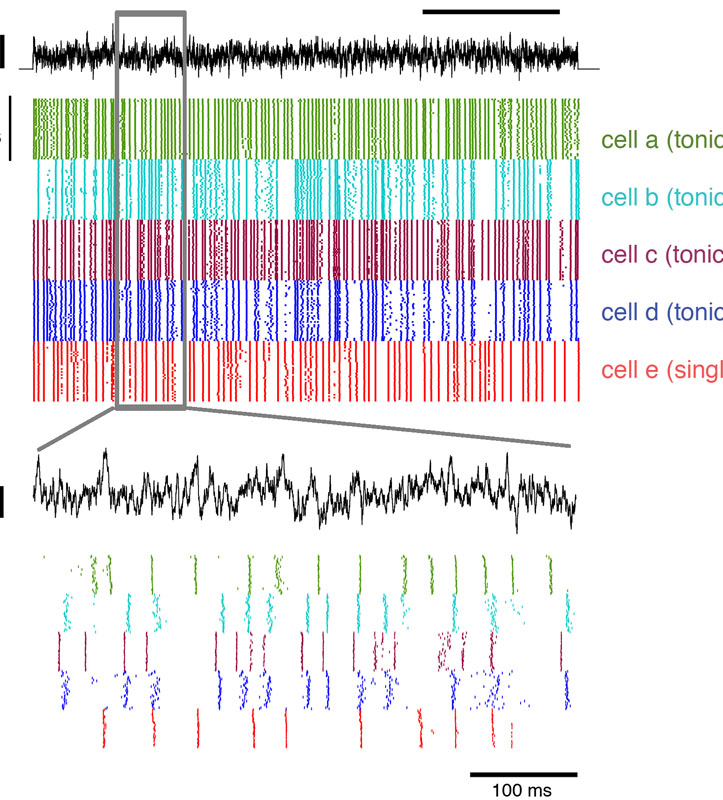 |
Ahn, J.A., Kreeger, L.J., Lubejko, S., Butts, D.A., and MacLeod, K.M. (2014) Intrinsic biophysical heterogeneity improves the population coding of temporal information. Journal of Neurophysiology 111:2320-2331 doi: 10.1152/jn.00836.2013 link |
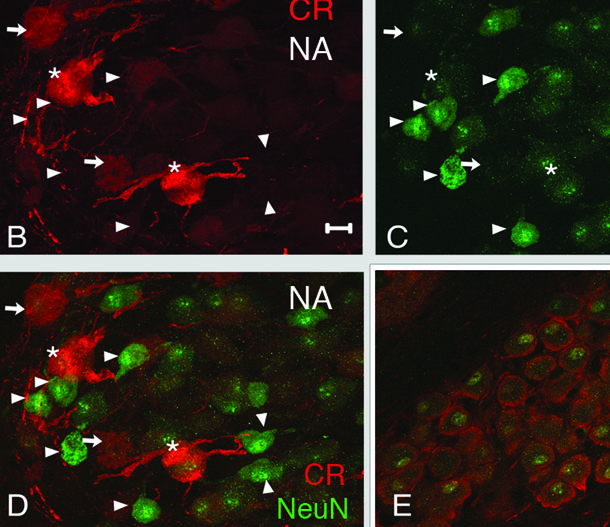 |
Bloom, S., Williams,A., MacLeod, K.M. (2014) Heterogeneous calretinin expression in the avian cochlear nucleus angularis. JARO 15:603-620 doi: 10.1007/s10162-014-0453-0 link |
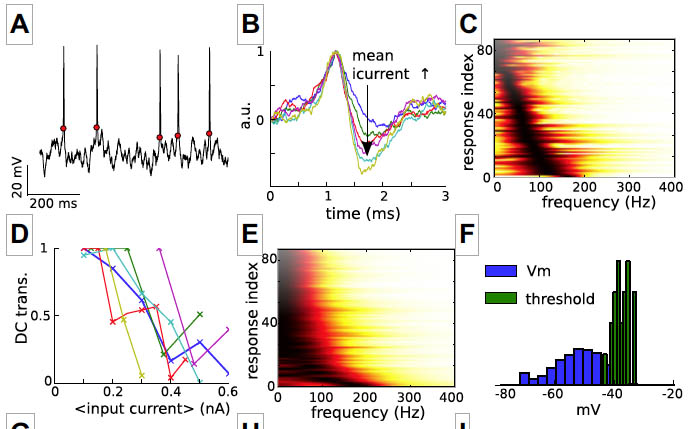 |
Fontaine, B., MacLeod, K.M., Lubejko, S.T., Steinberg, L.J., Koppl, C. and Pena, J.L. (2014) Efficient envelope extraction by adaptive spiking. Journal of Neurophysiology 112:430-445 doi:10.1152/jn.00132.2014 link |
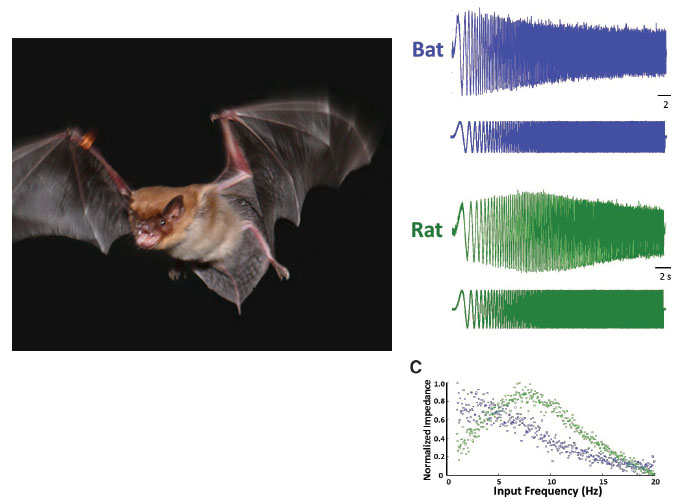 |
Heys, J.G, MacLeod, K.M., Moss, C.F., and Hasselmo, M.E. (2013) Bat and Rat Neurons Differ in Theta-Frequency Resonance Despite Similar Coding of Space. Science, 19 April 2013, v340(6130): 363-367. link |
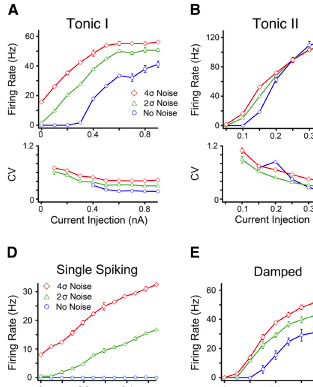 |
Kreeger, L.J., Arshed, A., and MacLeod, K.M. (2012) Intrinsic firing properties in the avian auditory brain stem allow both integration and encoding of temporally modulated noisy inputs in vitro. J. Neurophysiology v108(10):2794-2809, doi: 10.1152/jn.00092.2012, PMID:22914650 link |
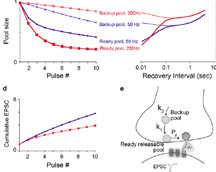 |
MacLeod, K.M. and Horiuchi, T. K. (2011) A rapid form of activity-dependent recovery from short-term synaptic depression in the intensity pathway of the auditory brainstem. Biological Cybernetics 104(3):209-23, doi: 10.1007/s00422-011-0428-8, PMID:21409439 link |
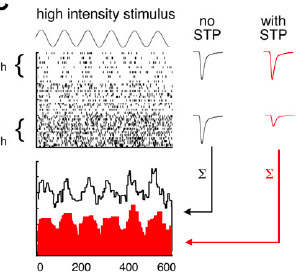 |
MacLeod, K. M. (2011) Short-term plasticity and intensity coding. Hearing Research, Special Issue on Synaptic and Intrinsic Plasticity, v 279(1-2): 13-21 doi:10.1016/j.heares.2011.03.001, PMID: 21397676 link |
 |
MacLeod, K.M. and Carr, C.E. (2011) Synaptic Coincidence Detection. In: Synaptic mechanisms in the auditory system. Series: Springer Handbook of Auditory Research, Trussell, L.O., Popper, A.N. and Fay, R.R. (Eds.). Springer Science + Business Media, LLC, New York. link |
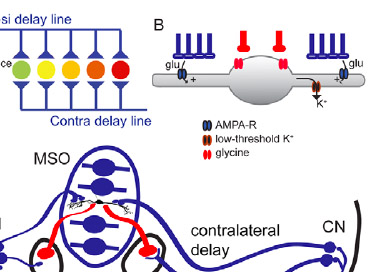 |
Carr CE, MacLeod KM (2010) Microseconds Matter. PLoS Biology 8(6): e1000405, PMID:20613856. link |
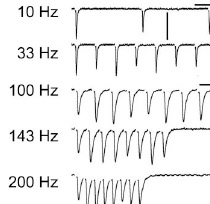 |
MacLeod KM, Horiuchi TK, Carr CE. (2007) A role for short-term synaptic facilitation and depression in the processing of intensity information in the auditory brainstem. J Neurophysiol. 97(4): 2863-74, PMID: 17251365 link |
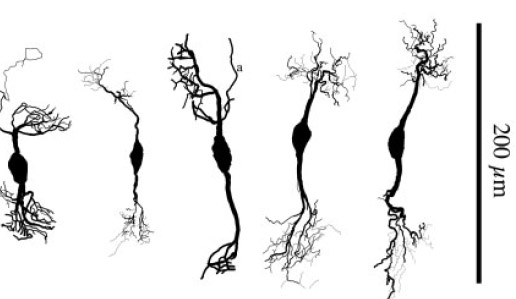 |
MacLeod KM, Soares, D, Carr CE (2006) Interaural timing difference circuits in the auditory brainstem of the emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). J. Comp Neurol. 495:185-201, PMID:16435285 link |
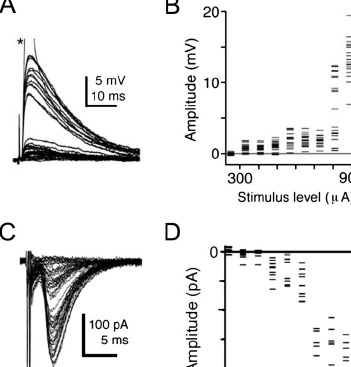 |
MacLeod KM, Carr CE (2005) Synaptic physiology in the cochlear nucleus angularis of the chick. J Neurophysiol. 93(5):2520-9, PMID: 15615833. link |
| Below are highlights from my past life as an olfaction researcher, but continues on theme of the cellular and ciruit mechanisms that neurons use to encode sensory stimuli: | |
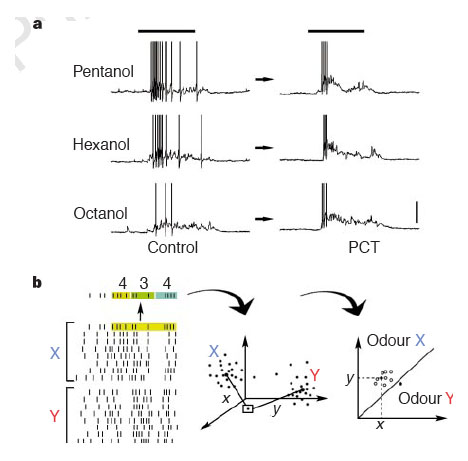 |
MacLeod, K., Bäcker, A., and Laurent, G. (1998) Who reads temporal information contained across synchronized and oscillatory spike trains? Nature 395:693-698. link |
 |
MacLeod, K., and Laurent, G. (1996) Distinct mechanisms for synchronization and temporal patterning of odor-encoding cell assemblies. Science 274:976-979 link |