Homework Assignment 2 - Descriptive Geometry
Due 9:30 am, Tuesday, September 17, 1996
Statement: Descriptive geometry represents the study of identify the relationships between the
geometric features in three-dimensional space and the basic geometric elements, such as points, lines, and
planes in two-dimensional space. Descriptive geometry serves as the foundation to formulate the
framework and algorithms in the CAD software development.
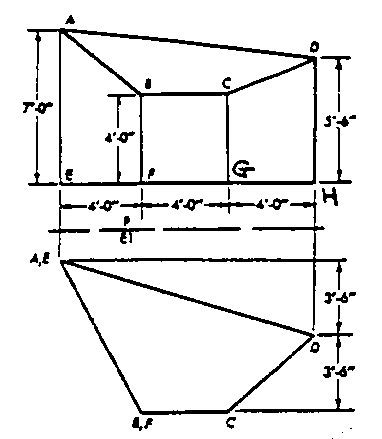
1. The hopper of an automatic coal stoker has been designed. It is shown in the following
figure. One of the design objectives is that coal remained in the hopper can be emptied
slowly and evenly. Before constructing the hopper, raw material has to be prepared. As
illustrated, four cylindrical columns made of steel, AE, BF, CG, and DH, are needed.
Four rectangular beams made of steel, AB, BC, CD, and AD, are needed. The top
surface, ABCD, should be covered by a sheet of steel.
Use spreadsheet to prepare a list indicating the true length of each of the four columns and
beams.
Calculate the weight of the top cover sheet, ABCD. Assume that the thickness of the steel
sheet is 1/4 of inch.
2. Two tubes AB and BC are to be connected by a third tube AC, thus completing the
circulation of air among the three locations, A, B and C. Note that location B is at the top
of a hill. The top of the hill is 8 ft east of A and 5 ft north of C. The slope of AB and BC
are 30 degrees and 45 degrees , respectively.
(1) Draw the front, top and right side views of the design configuration.
(2) Find the true length of the third tube AC.
(3) Find the true size of the angle for the special fitting.
3. The revolution method in descriptive geometry assumes that the observer is considered to
occupy a fixed position while the object is rotated into different positions to obtain
different views. Certain problems can be more easily solved by revolution. The following
problems to calculate the true length and slope of lines should be solved using the
revolution method. Verify your solutions with the direct method.