|
CodeMill Instruction Set Architecture
/* Load Instructions */
LDI: Immediate load; LDI R0,12; R0 = 12;
LDR: Relative load; LDR R0,5; R0 = RAM[PC +5]
LDD: Direct load: LDD R0,10; R0 = RAM[10];
LDT: Indirect load: LDT R0,10; R0 = RAM[RAM[10]];
LDG: Register load: LDG R0,R1; R0 = RAM[R1];
LDX: Index load: LDX R0,10,2; R0 = RAM[IX +10], IX = IX + 2;
LD+: Auto increment load: LD+ R0,R1; R0 = RAM[R1]; R1 = R1 + 1 (2, 4);
LD-: Autodecrement load: LD- R0,R1; R1 = R1 - 1 (2, 4); R0 = RAM[R1];
/* Store Instructions */
STI: Immediate store; STI 1,12; RAM[1] = 12;
STR: Relative store; STR R0,5; RAM[PC +5] = R0
STD: Direct store: STD R0,10; RAM[10] = R0;
STT: Indirect store: STT R0,10; RAM[RAM[10]] = R0;
STG: Register store: STG R0,R1; RAM[R1] = R0;
STX: Index store: STX R0,10,2; RAM[IX +10] = R0, IX = IX + 2;
ST+: Auto increment store: ST+ R0,R1; RAM[R1] = R0; R1 = R1 + 1 (2, 4);
ST-: Autodecrement store: ST- R0,R1; R1 = R1 - 1 (2, 4); RAM[R1] = R0;
Direct addressing does not support indexing- Indirect addressing does but with an extra instruction to increment a memory location, register
addressing allows indexing as well with an extra increment instruction, autoincrement and autodecrement register addressing allows indexing
without any extra operations.
/* Arithmetic Operations */
CLR: Clear; CLR R1; R1 = 0;
INC: Increment; INC R1; R1 = R1 + 1;
DEC:Decrement; DEC R1; R1 = R1-1;
NEG:Negate; NEG R1; R1 = -R1;
ADD: Add; ADD R1,R2; R1 = R1 + R2; or ADD R1,2; R1 = R1+2;
SUB: Subtract; SUB R1,R2; R1 = R1 - R2; or SUB R1,2; R1 = R1-2;
ADC: Add with carry; ADC R1,R2; R1 = R1 + carry;
SUC: Subtract with borrow; SUC R1,R2; R1 = R1 - R2 - borrow;
Examples will be given during class.
|
/* Branch Instructions */
/* Branch instructions in CodeMill are much more extensive than in Vesp. */
JMP D,address; go to address
JMP R,address; go to address + (PC)
JMP X,address; go to address + (IX)
JMP T,address; go to the address in the address
*/
/* >, =, <=, >=, <>
JCD Rx, <, number, label, register id,
address;
JCR Rx, <, number, label, register id,
address;
JCX Rx, <, number, label, register id,address;
JCT Rx, <, number, label, register id,address;
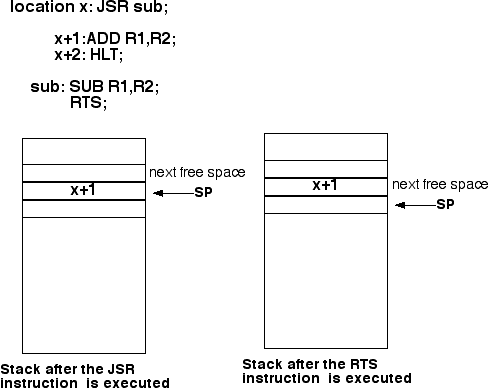
JSR subroutine name;
RTS; (Return from subroutine)
*/
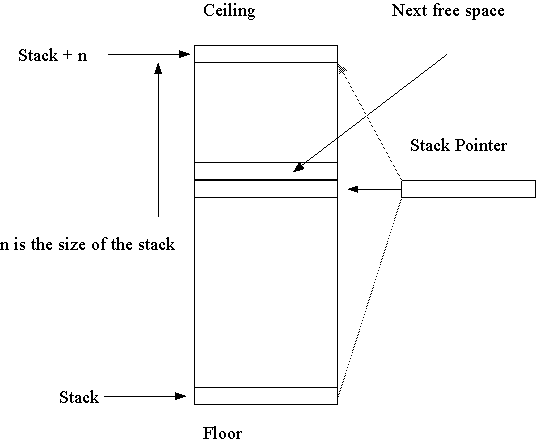
/* Stack Instructions */ PUS X, POP Y, CLS, ADS, SUS, NES, ORS, ANS, SRS,SLS, CMS,DUS, EXS Structure of A Stack
Conventions for pushing and popping values in and out of stack: ---SP points to currently occupied topmost location PUS: increment (or decrement SP) and push POP: pop and decrement (or increment SP) ---SP points to the next free location PUS: push and increment (or decrement SP) POP: decrement (or increment SP) and pop
Algebraic Trees
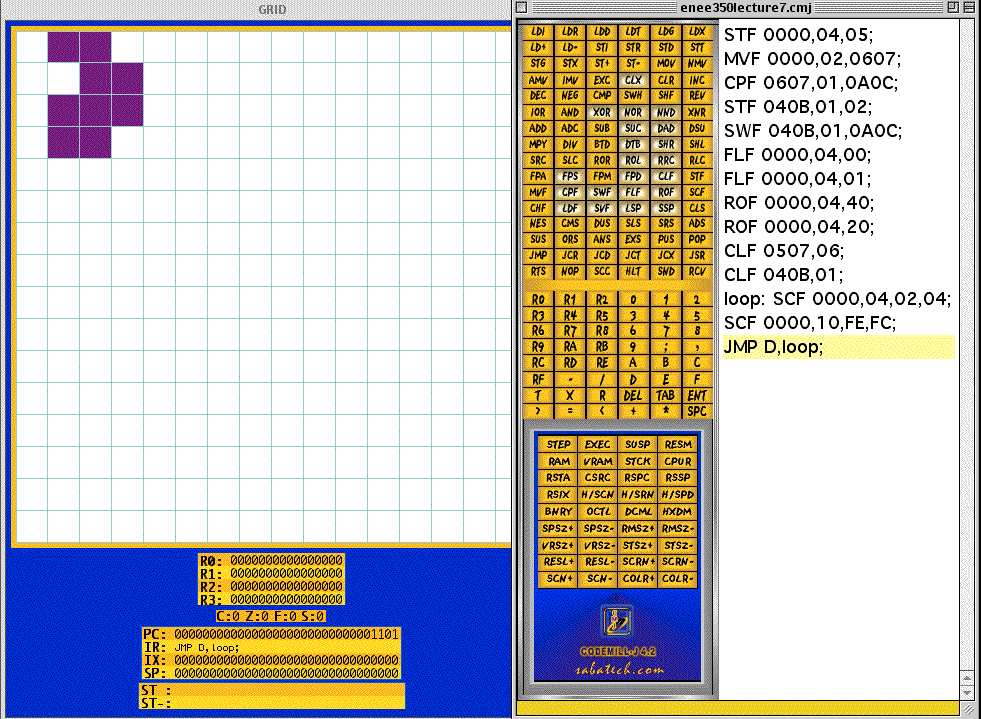
CLF Frame address, Frame size; STF Frame address, Frame size, Frame color; MVF Frame address, Frame size, Frame address; CPF Frame address, Frame size, Frame address; SWF Frame address, Frame size, Frame address; FLF Frame address, Frame size, Flip direction; ROF Frame address, Frame size, Rotation angle; SCF Frame address, Frame size, x-scale,y-scale; CHF Frame address, Character code, Character color; LDF Frame address, Frame size, Memory address; SVF Frame address, Frame size, Memory address; ----------------------------------------Examples-------------------------------------------- STF:Set Frame; STF 0000,02,03; Draw a 2x2 red square at x=0, y=0. CLF: Clear Frame; CLF 0102,04; Clears the 4x4 frame at location (2,4). MVF: Move Frame; MVF 0000,04,0607; Move the 4x4 square frame from location (0,0) to location (6,7). CPF: Copy Frame; MVF 0000,04,0607; Copy the 4x4 square frame at location (0,0) to location (6,7). SWF: Swap Frame; SWF 0000,04,0607; Swap the 4x4 square frame at location (0,0) with the 4x4 frame at location (6,7). When the frames overlap, the second frame paints over the firs frame. FLF: Flip Frame; FLF 0000,04,00; Flip the 4x4 frame at (0,0) about the y axis. FLF 0000,04,01; Flip the 4x4 frame at (0,0) about the x axis. ROF: Rotate Frame; ROF 0000,04,40; Rotate the 4x4 frame 90 degrees counterclockwise. Rotation angle = 360* p/256, where p denotes the 3rd argument in the ROF instruction. SCF: Scale Frame; SCF 0000, 04,02,04; Scale the 4x4 frame at (0,0) twice along the x axis and four times along the y axis. When the x or y scale value is negative, the frame is shrunk rather than magnified. For example, SCF 0000, 04,FE,FD; shrinks the 4-x4 frame at (0,0) twice along the x axis and three times along the y axis. LDF: Load Frame; LDF 0000,20,25; Loads the frame in memory locations 25 through 25+32-1 =56 to location (0,0) on the screen. SVF: Save Frame; LDF 0000,20,25; Save the 32x32 frame at location (0,0) into memory locations 25 through 25+32-1 =56. CHF: Character Frame; CHF 0000,31,0F; Draw 1 at location (0,0) in black. 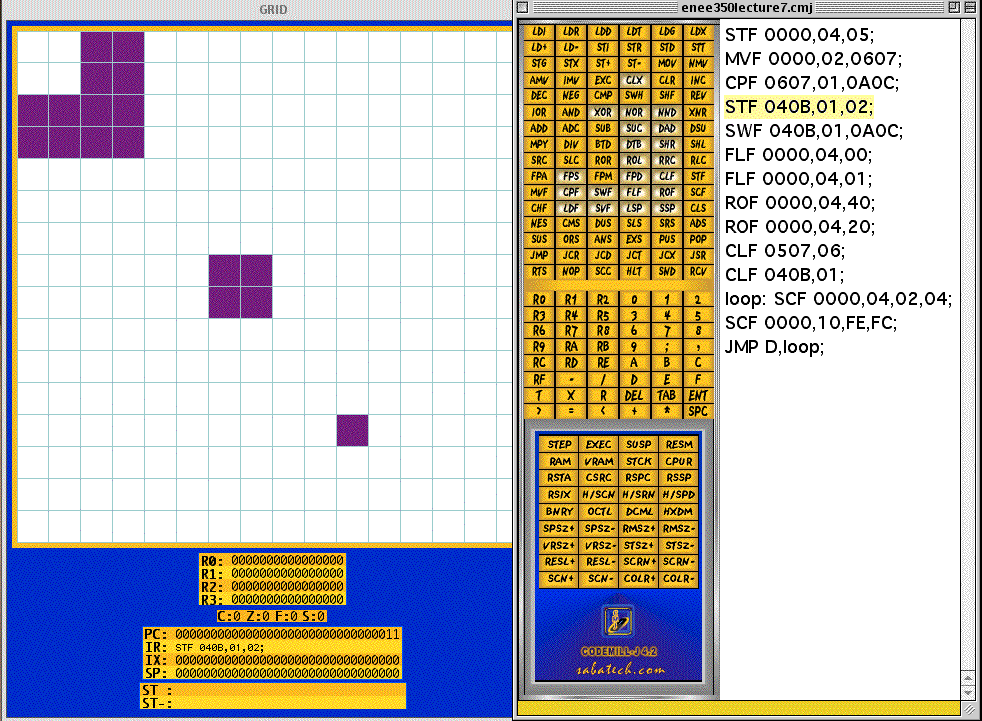
|
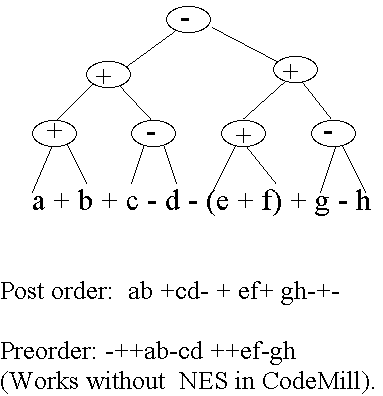 a: 1; /* Address 1 */
b: 2;
c: 3;
d: 4;
e: 5;
f: 6;
g: 7;
h: 8;
PUS h; PUS g;
SUS;
PUS f; PUS e;
ADS;
ADS;
PUS d; PUS c;
SUS;
PUS b; PUS a;
ADS;
ADS;
SUS;
/* Graphics Instructions */
a: 1; /* Address 1 */
b: 2;
c: 3;
d: 4;
e: 5;
f: 6;
g: 7;
h: 8;
PUS h; PUS g;
SUS;
PUS f; PUS e;
ADS;
ADS;
PUS d; PUS c;
SUS;
PUS b; PUS a;
ADS;
ADS;
SUS;
/* Graphics Instructions */