|
|
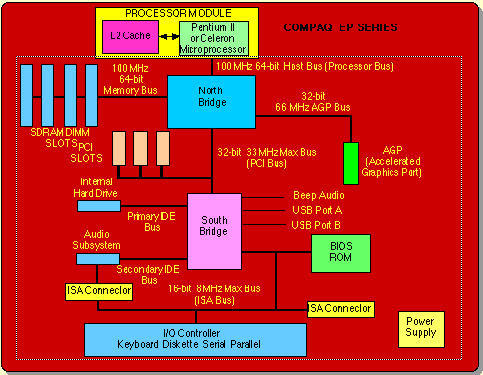
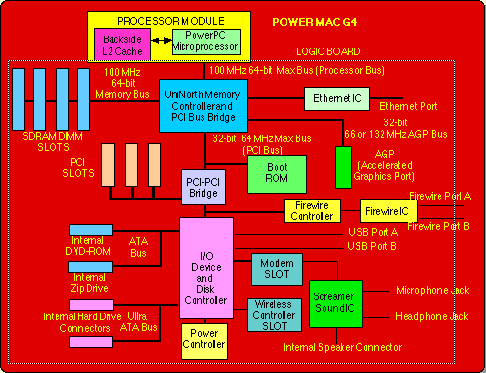
Memory space extends from the fastest (physically closest,smallest) to slowest (physicaly farthest, largest) to the CPU 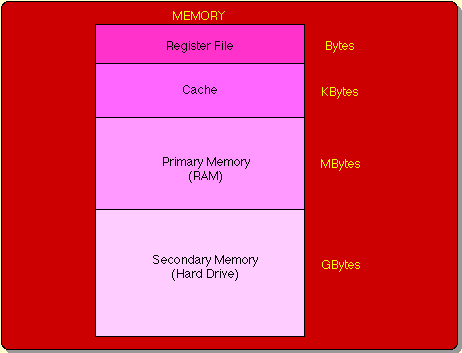 |
Register and some of the cache memory is glued to the Central Processor Unit (on board) whereas the primary and secondary memories as well as other input and output devices are interfaced to it by logic circuits and electrical wires,called buses. 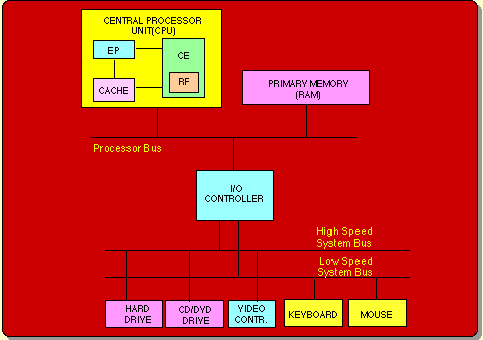 |
|
ISA: Industry Standard Architecture: A bus standard to connect PCs to its peripherals (slow speed: 8 MBytes/second)
24 address + 16 data + control + clock signals. (circuit switched)
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect: A bus developed by Intel for communication between CPU and its peripherals
(high speed: up to 1 GByte/second) 32-bit multiplexed address/data + control + clock
(pseudo-circuit switched)
USB: Universal Standard Bus (Faster than ISA and more flexible- 12 to 480 MBits/second)- VCC,
GND, D+, D- (packet-switched) |
|
|
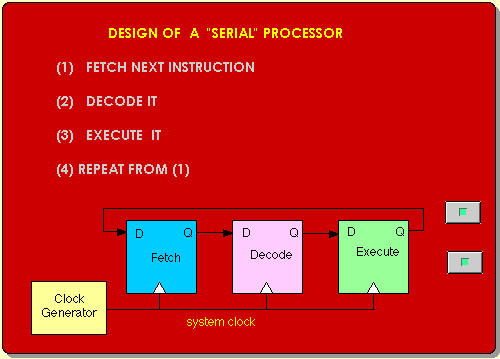 |
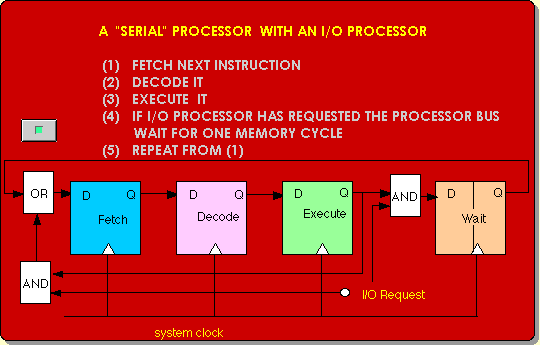 |
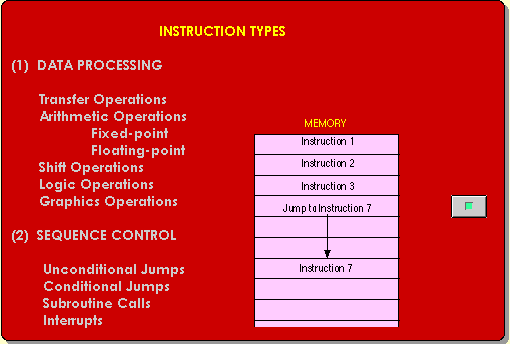 |
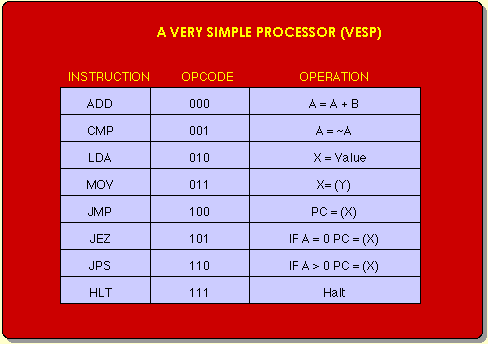 |
|
|
|
|
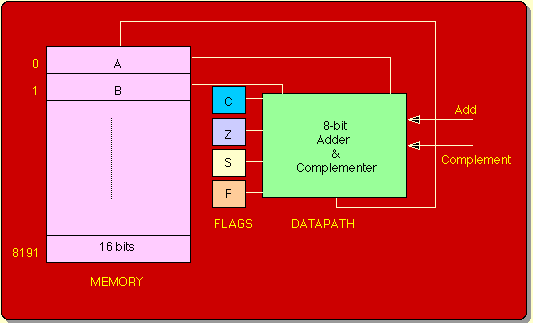 |
|
|