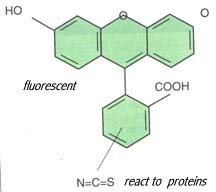
Lab 8 Conjugation of Antibody with FluoresceinAntibodies can be covalently coupled to a variety of enzymes and fluorochromes as well as solid support like Sepharose beads for uses of immunological detection assays. Antibodies conjugated with fluorochromes can be used for immunofluorescence analyses. Antibodies conjugated with enzymes are widely used in Western blot and Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA). Antibodies conjugated with Sepharose beads are used for affinity chromatography and immunoprecipitation. You will learn how to carry out these assays using conjugated antibodies in the rest of semester. In this lab exercise, you will learn how to make antibody conjugates. A simple procedure will be used to coupling fluorochrome, fluorescein, to an antibodies that can be used for direct immunofluorescent testing. First, antibody is coupled to the fluorescent dye, fluorescein isothiocyanate, through a chemical reaction. Then, the conjugated antibody will be separated from and dye molecules by equilibrium dialysis.
Equilibrium dialysis is a method to separate the large protein molecules, such as the fluorescein-conjugated antibody, from small molecules, such as fluorescein isothiocyanate that has not reacted with the antibody. The reaction mixture will be put into membrane tubing. Dialysis tubing is a semipermeable cellulose membrane that allows the separation of molecules by diffusion. The tubing is manufactured in various pore-size. When the dialysis tubing with the reaction mixture is placed into a buffer solution, the small molecules will freely pass through the pores and into the buffer by diffusion, while the large antibody proteins will remain trapped inside. Small molecules will stop diffusing when their concentration reaches equilibrium on both sides of the membrane. By changing buffer solution for three or four times, most of the small molecules can be removed from the mixture.
Material
1 ml of antibody as 2 mg/ml in 20 mM carbonate buffer, pH 8.5
2 ml of fluorescein isothiocyanate isomer 1 as 1 mg/ml in the carbonate buffer
Dialysis tubing and clamps
dH2O in beakersProcedure
1. Add 1 ml of fluorescein isothiocyanate to 1 ml of antibody. Wrap the tube in foil and rotate continuously for 30 min at room temperature.
2. During the incubation, prepare the dialysis tubing. Boil the dialysis tubing in dH2O for 15 min. Rinse the tubing and clamps with dH2O. Clamp one end of the tubing.
3. After the incubation, remove the foil and centrifuge the mixture for 3 min at 500xg.
4. Carefully transfer the supernatant to a dialysis tube and discard the pellet. Clamp the other end of the dialysis tube. Put the dialysis tube into 1 l of dH2O.
5. As a control, put 1 ml of fluorescein isothiocyanate into a new dialysis tube. Clamp the other end of the dialysis tube and put it into 1 l of d H2O in a separated container.
6. The samples are dialyzed against dH2O over night at 4oC with dH2O being changed for at least 3 times.
7. On March 5, please observe the color of the solution in the dialysis tubes to see which one still has the fluorescein color, and explain why.
Study Questions
1. What is the purpose of the dialysis tubing used in the preparation of FITC-conjugated antibody? What remained in the tubing after dialysis?
2. Starting from next lab exercise, you should identify what kind of antibody conjugate that is used for each lab exercise and remember the applications of each type of antibody conjugate.