 Homework Assignment 5
Homework Assignment 5
 Homework Assignment 5
Homework Assignment 5
Due: 9am, December 8, 2008.
This assignment will give you practice at writing Java program that contain:
Solve problems 34, 35 and 37 in the Java Programming Exercises + the egg mesh problem below.
Graphical Display and Engineering Property Calculation for Egg Mesh
The adjacent figure shows a screendump of an egg mesh.
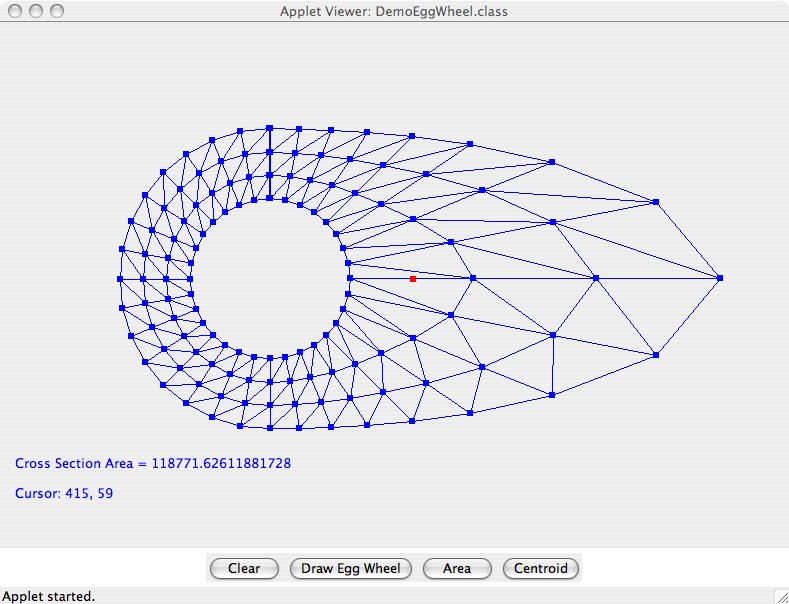
Figure. Screendump of egg mesh.
The left-hand side of the mesh is essentially a wheel, with constant inside and outside diameters. The right-hand side of the mesh is a composition of two shapes. The inner boundary is a circle. The outer boundary is an ellipse. The left and right-hand sides have compatible dimensions. The red dot shows the position of the centroid.
To get started:
Things to do:
for ( int i = 1; i <= iNoAngularIntervals; i = i + 1 ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= iNoRadialIntervals; j = j + 1 ) {
double dTheta1 = ((i-1)/((double) iNoAngularIntervals))*2.0*Math.PI;
double dTheta2 = (i/((double) iNoAngularIntervals))*2.0*Math.PI;
double dMinRadius = dMinWheelRadius +
(j-1)/((double) iNoRadialIntervals)*(dMaxWheelRadius-dMinWheelRadius);
double dMaxRadius = dMinWheelRadius +
(j)/((double) iNoRadialIntervals)*(dMaxWheelRadius-dMinWheelRadius);
// Create first triangle ....
// Create second triangle ....
}
}
and simple formula for the angles and radaii at each increments of the geometry generation. Notice that dMinRadius and dMaxRadius to not depend on dTheta1 and dTheta2.
To generate the egg geometry, you will need separate dMinRadius and dMaxRadius values for dTheta1 and dTheta2. Also, you will need to separate the geometry generation into two parts: (1) the half circle, and (2) the half egg. I did this by adding a branching construct to the body of the loops, i.e.,
for ( int i = 1; i <= iNoAngularIntervals; i = i + 1 ) {
for ( int j = 1; j <= iNoRadialIntervals; j = j + 1 ) {
double dTheta1 = ((i-1)/((double) iNoAngularIntervals))*2.0*Math.PI;
double dTheta2 = (i/((double) iNoAngularIntervals))*2.0*Math.PI;
if ( dTheta1 <= Math.PI && dTheta2 <= Math.PI ) {
dRadius1 = .....
dRadius2 = .....
} else {
dRadius1 = dRadius2 = dMaxWheelRadius;
}
double dMinRadius1 = .....
double dMinRadius2 = .....
double dMaxRadius1 = .....
double dMaxRadius2 = .....
// Create first triangle ....
// Create second triangle ....
}
}
public double getCentroidX() { ....
public double getCentroidY() { ....
to the class DemoGraphicsScreen. You can find the relevant details in the Footprint program. I would put these methods immediately below the method area().
public void gsDrawCentroid() { ....
to compute and display the centroid. You might find the couple of lines:
// Display of centroid on canvas ...
g2D.setColor( Color.red );
g2D.fillRect( (int) (getCentroidX()-3), (int) (getCentroidY()-3), 6, 6);
useful. Connect the "button event code" to gsDrawCentroid(). Now everything should work!
Points to note:
/*
* =============================================================
* RainfallAnalysis.java: The java program conducts a simple
* statistical analysis on monthly rainfall measurements.
*
* Written By: Mark Austin November 2005
* =============================================================
*/
import java.lang.Math;
public class RainfallAnalysis {
// No of columns in print array task...
public final static int NoColumns = 6;
// =========================================================
// main method : this is where the program execution begins.
// =========================================================
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
// [a] Populate rainfall data array (measured over 30 days)
float [] fRainfall = { 1.1F, 0.8F, 1.1F, 1.2F, 0.5F, 0.2F,
0.05F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.4F, 0.5F,
0.6F, 0.8F, 1.0F, 1.2F, 3.0F, 2.4F,
1.5F, 1.0F, 1.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F,
0.0F, 0.0F, 0.0F, 2.0F, 2.0F, 2.4F };
// [b] Print contents of fRainfall in six columns ...
System.out.println("Array: fRainfall");
System.out.println("----------------");
for (int i = 1; i <= fRainfall.length; i = i + 1) {
System.out.printf( " %4.2f", fRainfall [i-1] );
if (i % NoColumns == 0 || i == fRainfall.length )
System.out.println("");
}
System.out.println("----------------");
// [b] Compute and print rainfall measurement statistics..
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Statistics of Daily Rainfall");
System.out.println("============================");
System.out.printf("Max value = %5.2f\n", maxValue( fRainfall ));
System.out.printf("Min value = %5.2f\n", minValue( fRainfall ));
System.out.printf("Range of values = %5.2f\n", range( fRainfall ));
System.out.printf("Mean value = %5.2f\n", mean( fRainfall ));
System.out.printf("Standard deviation = %5.2f\n", std( fRainfall ));
System.out.println("============================");
}
/* ================================================== */
/* Methods to compute maximum/minimum daily rainfalls */
/* ================================================== */
public static float maxValue ( float fA [] ) {
float fMax = fA[0];
for (int i = 0; i < fA.length; i = i + 1)
fMax = Math.max( fMax, fA [i] );
return fMax;
}
public static float minValue ( float fA [] ) {
float fMin = fA[0];
for (int i = 0; i < fA.length; i = i + 1)
fMin = Math.min( fMin, fA [i] );
return fMin;
}
/* ========================================== */
/* Method to compute range in daily rainfalls */
/* ========================================== */
public static float range ( float fA [] ) {
return ( maxValue (fA) - minValue(fA) );
}
/* ====================================================== */
/* Compute mean and standard deviation of daily rainfalls */
/* ====================================================== */
public static float mean ( float fA [] ) {
float fSum = 0.0F;
for (int i = 0; i < fA.length; i = i + 1)
fSum = fSum + fA[i];
return fSum/fA.length;
}
public static float std ( float fA [] ) {
float fMean = mean ( fA );
float fSum = 0.0F;
for (int i = 0; i < fA.length; i = i + 1)
fSum = fSum + fA[i]*fA[i];
return (float) Math.sqrt(fSum/fA.length - fMean*fMean);
}
}
You should find that the data array version of the rainfall analysis is much shorter!!
Note. For each problem, hand in a copy of your program source code and a script of I/O for typical program usage.
If you are working on UNIX/Mac OS X then the procedure for creating a script is easy -- just type something like:
prompt >> script output-file
Now all input/output on the screen will be echoed to the file "output-file". To terminate the script, type:
prompt >> exit
Now print "output-file" and hand it in.
If you are working on Windows, just cut-and-paste the output into a Word document.
Developed in October 2008 by Mark Austin
Copyright © 2008,
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Maryland