 Homework Assignment 5
Homework Assignment 5
 Homework Assignment 5
Homework Assignment 5
Due: December 11, 2006.
No extensions -- this is the last day of class.
This assignment will give you practice at writing Java programs that create and manipulate objects.
A data array class is a one dimensional array of floating-point numbers bundled together with methods to compute statistics on the stored values (e.g., maximum value, minumum value).
Download, compile, and run the DataArray java code from the "java examples" web page. Rewrite the rainfall analysis program (i.e., RainfallAnalysis.java) so that it uses the DataArray facilities.
Hint
Your solution will have two source code files:
DataArray.java and RainfallAnalysis.java. Don't change any of the
code in DataArray.java -- just write a new version of RainfallAnalysis.java.
The files before and after compilation should be:
Before --> javac RainfallAnalysis.java --> After
===================== =====================
RainfallAnalysis.java RainfallAnalysis.java
DataArray.java DataArray.java
RainfallAnalysis.class
DataArray.class
===================== =====================
You should find that your implementation for this assignment is considerably shorter than in Assignment 4.
Solve Problem 28 in the "Java Programming Exercises" handout.
Hint.
You need to remember that all of the arithmetic in this problem
needs to work with complex numbers. Hence, suppose that you
want to compute the roots to the equation:
2 x^2 - 3 x + 2 = 0.0
where the coefficients are all real numbers. Here, you need to implement the equation as if it were written:
(2+0i) x^2 - (3+0i) x + (2+0i) = 0.0
Your solution should consist of two files: Complex.java and Quadratic.java. You can download Complex.java from the class web site. Quadratic.java will simply call the methods in Complex.java ... therefore, there is no need to change the contents of Complex.java.
Suppose that you have been asked to create a simplified model of "a person" that might one day be used in an imigration/employee database.
Individuals are defined by their name, gender, nationality, social security number (if living in the USA), date of birth, and if applicable, date at which they died. Many other characteristics are also used -- for example, height, weight, hair/eye color, picture, and finger print.
From a programming perspective, the design and implementation of such a model is quite challenging. First, the attributes of a person involve various kinds of data. To capture height and weight, a good implementation needs to include units of measurement (e.g., inches, cm). A good implementation will also need to work with dates and calendars because some of these attributes change with time (e.g., tomorrow you will be one day older than you are today).
A suitable (abbreviated) class declaration might be as follows:
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class Person {
String sFirstName; // First name ...
String sFamilyName; // Family name ...
String gender; // Gender ('M' or 'F') ....
String sNationality; // Nationality ....
boolean criminalRecord; // Does the person have a criminal record? ....
int iSsn; // Social security number ....
Date dob; // Date of birth ....
Date dod; // Date of death ....
... fill in details here ....
}
A first-cut implementation would include the following methods:
public void setName( String sName ); // Set name ...
public void getName( String sName ); // Get name ...
public void setGender( String gender); // Set (M or F) gender of individual...
public String getGender(); // Retrieve gender of individual..
public void setBirth( Date dob ); // Set date of birth ...
public Date getBirth( Date dob ); // Get date of birth ...
public int getAge(); // Retrieve age of individual ...
public String toString(); // Create string representation of person ...
Fill in the missing details for Person.java. Develop a main() method to exercise (and test) each of the methods in Person.java. I suggest that you create a string description of a person in toString().
If you think that the class definition is inadequate, then by all means please go ahead and extend it -- put a note on your homework indicating why you made the change.
Hints ....
Computing the age of a person requires a pretty detailed knowledge of the Date and Calendar classes, so here's a big hint!!
/*
* =================================================================
* Person.java. Create person objects and compute their age...
*
* Written By: Mark Austin December 2006
* =================================================================
*/
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class Person {
protected Date birthdate;
// ==============================================================
// Compute age of a person ...
// ==============================================================
public int getAge() {
// Calendar objects for "today" and "date of birth"...
Calendar today = Calendar.getInstance();
Calendar birthday = new GregorianCalendar();
birthday.setTime( birthdate );
// Compute basic difference in years ....
int yearDiff = today.get( Calendar.YEAR ) - birthday.get( Calendar.YEAR );
// Birthday still needs to occur this year...
if ( today.get(Calendar.MONTH) < birthday.get(Calendar.MONTH) )
yearDiff = yearDiff - 1;
else if (today.get(Calendar.MONTH) == birthday.get(Calendar.MONTH) &&
today.get(Calendar.DATE) < birthday.get(Calendar.DATE) ) {
yearDiff = yearDiff - 1;
}
return yearDiff;
}
public void setBirthDate(Date aBirthDate) {
this.birthdate = aBirthDate;
}
public void setBirthDate(int iYear, int iMonth, int iDay ) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.set( iYear, iMonth, iDay );
this.birthdate = cal.getTime();
}
public Date getBirthDate() {
return birthdate;
}
// ==========================================================
// Exercise methods in Person class ....
// ==========================================================
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
Person homer = new Person();
homer.setBirthDate ( 1956, Calendar.JANUARY, 1 );
System.out.println("Homer's age is: " + homer.getAge() );
Person bart = new Person();
bart.setBirthDate ( 1985, Calendar.APRIL, 1 );
System.out.println("Bart's age is: " + bart.getAge() );
}
}
When I compile and run the code I get:
Script started on Fri Dec 01 12:57:11 2006 prompt >> java Person Homer's age is: 50 Bart's age is: 21 prompt >> prompt >> exit Script done on Fri Dec 01 12:57:17 2006
With the source code for modeling a person in place (see the previous question), now it's now time to move onto modeling a family.
Families are defined by relationships among people (i.e. the Relatives).
Each family member will one mother and one father,
zero or more siblings and children, and possibly a spouse.
Other relationships like brother, sister, husband/wife,
grandparents and cousins can be computed.
They need not be explicitly defined.

Modeling the Simpsons
The Simpsons are one of America's most famous families
(for details, see the
wikipedia writeup on Homer Simpson).
For this question, let us make the following assumptions:
Full Name Gender Dob Relation to Homer
----------------------------------------------------------------
Homer Simpson Male 1/1/1956 ......
Marge Simpson Female 1/1/1960 Wife
Bart Simpson Male 4/1/1985 Son
Lisa Simpson Female 4/1/1987 Daughter
Maggie Simpson Female 6/1/1995 Daughter
Mona Simpson Female 1/1/1936 (Deceased) Mother
Abraham Simpson Male 1/1/1911 Father
Herb Powell Male 1/1/1957 Half-brother
----------------------------------------------------------------
Your answer to this question should be composed of four files: (1) Person.java, (2) FamilyMember.java, (3) Relatives.java, and (4) SimpsonFamily.java. The relationships among these classes should be as shown in Figure 1:
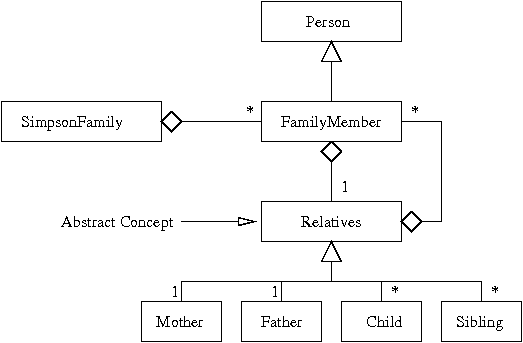
Figure 1.
UML class diagram for relationships among Person, FamilyMember,
Relations and SimpsonFamily classes.
In simple terms, Figure 1 says:
Relatives is a generalized (or abstract) concept for the set of family members that fullfil the roles of father, mother, spouse, children and siblings.
Things to do:
A suitable starting point is:
public class FamilyMember extends Person {
Relatives theRelatives;
... fill in details here ....
public String toString() { ... }
public static void main( String [] args ) { ... }
}
public class Relatives {
FamilyMember mother;
FamilyMember father;
FamilyMember spouse;
Arraylist siblings;
Arraylist children;
... fill in additional details here ....
public String toString() { ... }
public static void main( String [] args ) { ... }
}
Add data and methods for the relationships (e.g., adding a new child to the list of children) required by the class definitions.
Use the main() method in each class to fully exercise and test the relationships that can be supported by the class.
A BIG HINT!!
Here are outlines of my solution ...
FamilyMember.java
/*
* =================================================================
* FamilyMember.java. A family member is a person who has relatives.
*
* Written By: Mark Austin December 2006
* =================================================================
*/
import java.lang.Math.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.text.*;
public class FamilyMember extends Person {
protected Relatives theRelatives;
// ==========================================================
// Family member constructor ....
// ==========================================================
public FamilyMember() {
theRelatives = new Relatives();
}
// ==========================================================
// Setup/retrieve family relationships ....
// ==========================================================
public void setFather( FamilyMember father ) {
theRelatives.father = father;
}
... fill in details here ...
// ==========================================================
// Create a String description of a family member...
// ==========================================================
public String toString() {
// Basic family member information ....
... fill in details here ...
// Add information on the relatives ...
... fill in details here ...
return s;
}
// ==========================================================
// Exercise methods in Familymember class ....
// ==========================================================
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
// Create a handful of person objects ...
FamilyMember homer = new FamilyMember();
homer.setName("Homer Simpson");
homer.setBirthDate ( 1956, Calendar.JANUARY, 1 );
... fill in details here ...
// Setup Homer's family relations
homer.setFather( abe );
... fill in details here ...
// Setup Bart's family relations
... fill in details here ...
// Print family relations for Homer and Bart ...
... fill in details here ...
}
}
Relatives.java
/*
* ====================================================================
* Relatives.java. Model common relationships among people in a family.
*
* Written By: Mark Austin December 2006
* ====================================================================
*/
import java.lang.Math.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.text.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class Relatives {
FamilyMember mother;
FamilyMember father;
FamilyMember spouse;
ArrayList siblings = new ArrayList();
ArrayList children = new ArrayList();
// ==========================================================
// Class constructors ...
// ==========================================================
public Relatives () {
this.mother = null;
this.father = null;
this.spouse = null;
}
// ==========================================================
// Setup/retrieve family relationships ....
// ==========================================================
public void setFather( FamilyMember father ) {
this.father = father;
}
... fill in details here ...
// ==========================================================
// Create a String description of a persons cridentials
// ==========================================================
public String toString() {
String s = "";
// Get father and mother ....
... fill in details here ....
// Get spouse ....
... fill in details here ....
// Retrieve list of siblings and children ....
... fill in details here ....
return s;
}
// ==========================================================
// Exercise methods in Relatives class ....
// ==========================================================
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
// Create 4-5 family members ....
FamilyMember homer = new FamilyMember();
homer.setName("Homer Simpson");
homer.setBirthDate ( 1956, Calendar.JANUARY, 1 );
... fill in details here ...
// Setup and print Homer's family relations
... fill in details here ...
}
}
SimpsonFamily.java
/*
* =====================================================================
* SimpsonFamily.java. Create an array list of family member objects.
* Order the family members according to age,
* youngest first.
*
* Written By: Mark Austin December 2006
* =====================================================================
*/
import java.util.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class SimpsonFamily {
ArrayList member = new ArrayList();
// Sort family members by age ....
public void sortByAge () {
Collections.sort( member, new ageCompare() );
}
class ageCompare implements Comparator {
public int compare( Object o1, Object o2) {
Person p1 = (Person) o1;
Person p2 = (Person) o2;
if ( p1.getAge() == p2.getAge() )
return 0;
else if ( p1.getAge() > p2.getAge() )
return 1;
else
return -1;
}
}
// ==========================================================
// Systematically assemble details of the Simpson Family...
// ==========================================================
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
// Create family member objects ....
FamilyMember homer = new FamilyMember();
homer.setName( "Homer Simpson" );
homer.setGender( "Male" );
homer.setBirthDate ( 1956, Calendar.JANUARY, 1 );
.... fill in details here ....
// Setup family relations.....
.... fill in details here ....
// Create an arraylist of Simpson family members ...
SimpsonFamily simpson = new SimpsonFamily();
simpson.member.add( homer );
.... fill in details here ....
// Walk along list and print details ....
System.out.println("Meet The Simpsons! ");
System.out.println("=============================");
.... fill in details here ....
// Sort family members by age .....
.... fill in details here ....
// Print sorted list .....
System.out.println("Order: From youngest to oldest ... ");
System.out.println("==================================");
.... fill in details here ....
}
}
ABBREVIATED OUTPUT
Here is what I have:
Script started on Tue Dec 5 18:20:09 2006 prompt >> prompt >> java SimpsonFamily Meet The Simpsons! ============================= Name: Homer Simpson Age: 50 Gender: Male Father: Abe Simpson Spouse: Marge Simpson Children: Bart Simpson, Lisa Simpson, Maggie Simpson .... details on Marge, Abe, Bart and Lisa removed ... Name: Maggie Simpson Age: 11 Gender: Female Father: Homer Simpson Mother: Marge Simpson Siblings: Bart Simpson, Lisa Simpson Order: From youngest to oldest ... ================================== Name: Maggie Simpson Age: 11 Gender: Female Father: Homer Simpson Mother: Marge Simpson Siblings: Bart Simpson, Lisa Simpson Name: Lisa Simpson Age: 19 Gender: Female Father: Homer Simpson Mother: Marge Simpson Siblings: Bart Simpson, Maggie Simpson Name: Bart Simpson Age: 21 Gender: Male Father: Homer Simpson Mother: Marge Simpson Siblings: Lisa Simpson, Maggie Simpson Name: Marge Simpson Age: 46 Gender: Female Spouse: Homer Simpson Children: Bart Simpson, Lisa Simpson, Maggie Simpson Name: Homer Simpson Age: 50 Gender: Male Father: Abe Simpson Spouse: Marge Simpson Children: Bart Simpson, Lisa Simpson, Maggie Simpson Name: Abe Simpson Age: 95 Gender: Male Child: Homer Simpson prompt >> prompt >> exit Script done on Tue Dec 5 18:20:20 2006
Note. For each problem, hand in a copy of your program source code and a script of I/O for typical program usage. To create a script, type something like:
prompt >> script output-file
Now all input/output on the screen will be echoed to the file "output-file". To terminate the script, type:
prompt >> exit
Now print "output-file" and hand it in.
Developed in November 2006 by Mark Austin
Copyright © 2006, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Maryland