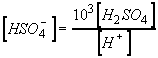
Substitute eq 1 into 2:
Concentration of Sulfate :
H2SO4(l) + H2O(l) --> H3O+(aq)
+ HSO4- (aq)
Here, we save space by omitting H2O and using H+ instead of the hydronium ion.
The equations needed are:
Equilibrium equations:
1) An expression for Ka1
2) An expression for Ka2
Water ionization
3) [H+][OH-] = 10-14
Electroneutrality equation
4) [H+] = [HSO4-] + 2[SO4-2]+[OH-]
Mass balance
5) [H2SO4] + [HSO4-] + [SO4-2]
= 1.7x10-5 M
Status : Five unknowns, and five knowns. There seem to
be a variety of strategies; let's focus on the charge balance equation.
Replace all non-hydrogen terms. Since the sulfate is the "farthest"
from H+, let's start with it:
Rearrange eq 1:
Substitute eq 1 into 2:
Solve for sulfate concentration:
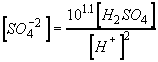
Now, substitute eqs 1, 3, and 6 into the charge balance equation, eq 4.
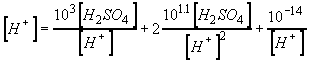
We need a relationship between H+ and H2SO4.
It's time to turn to eq 5.
Substitute eq 1 and eq 6 into eq 5:
and solve for H2SO4:
and you can find the solution by determining the zero crossing point of
the two equation.
An Easier way is to assume that as the pH will be acid (<<4) then:
[H2SO4] - 0
[OH-] <<<< [H+]
MB : 1.5x10-5 M = [HSO4-] + [SO4-2]
-- [SO4-2] = 1.5x10-5 M - [HSO4-]
PBE : [H+] = [HSO4-] + 2[SO4-2] - [HSO4-] = [H+] - 2(1.5x10-5 M - [HSO4-])
[HSO4-] = 2(1.5x10-5 M)- [H+]
and then
quadratic equation, [H+] = 3.4x10-5 - pH
= 4.4